Stress management encompasses a holistic approach to mitigating the adverse effects of stress on both mental and physical well-being. It involves recognizing stress triggers and implementing strategies to cope with them effectively. This can include adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, nutritious eating habits, and sufficient sleep. Additionally, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga help calm the mind and reduce tension in the body. Effective time management, setting boundaries, and seeking social support are crucial in managing stress levels. Engaging in hobbies and interests provides a positive outlet for stress, while limiting exposure to stressful stimuli and cultivating mindfulness promotes a sense of inner peace and resilience. Seeking professional help when needed ensures individuals receive tailored support and coping mechanisms. By incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals can build resilience and maintain a balanced, stress-free lifestyle.

Causes of stresss
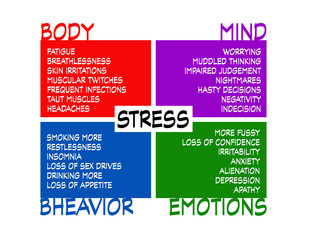
Stress can stem from a myriad of sources, both external and internal, often resulting from the demands and pressures of daily life. External factors such as work-related issues, financial difficulties, relationship conflicts, or major life changes like moving to a new city or starting a new job can trigger stress. Additionally, environmental stressors like noise pollution, overcrowding, or traffic congestion can contribute to feelings of tension and unease. Internally, unrealistic expectations, perfectionism, negative self-talk, or a lack of assertiveness can intensify stress levels. Furthermore, physical factors such as illness, injury, or hormonal imbalances can exacerbate stress responses.

Effects of stress
The effects of stress permeate every aspect of an individual’s life, impacting both mental and physical well-being. Prolonged exposure to stress can lead to a range of adverse consequences. On a mental level, stress often manifests as heightened anxiety, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and feelings of overwhelm. Chronic stress can contribute to mood disorders such as depression and exacerbate existing mental health conditions. Moreover, stress can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or other sleep disturbances, which further exacerbates mental and emotional strain. Physically, stress triggers the body’s “fight or flight” response, releasing hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can elevate heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension.